In the rapidly evolving world of AI applications, Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful pattern for enhancing Large Language Models (LLMs) with up-to-date, domain-specific knowledge. This article walks through building a production-ready RAG ingestion pipeline using AWS services that automatically fetches news from RSS feeds and syncs them with an AWS Bedrock Knowledge Base.
The RAG Architecture Challenge#
When implementing RAG systems, the ingestion pipeline is often overlooked but critically important. A well-designed pipeline should:
- Automatically retrieve fresh content from reliable sources
- Process and structure the content appropriately
- Efficiently sync data with your vector database or knowledge base
- Handle errors gracefully and provide operational visibility
- Scale with your needs while remaining cost-effective
Let’s examine a real-world implementation that addresses these challenges.
System Architecture Overview#
The system consists of two Lambda functions orchestrated by EventBridge:
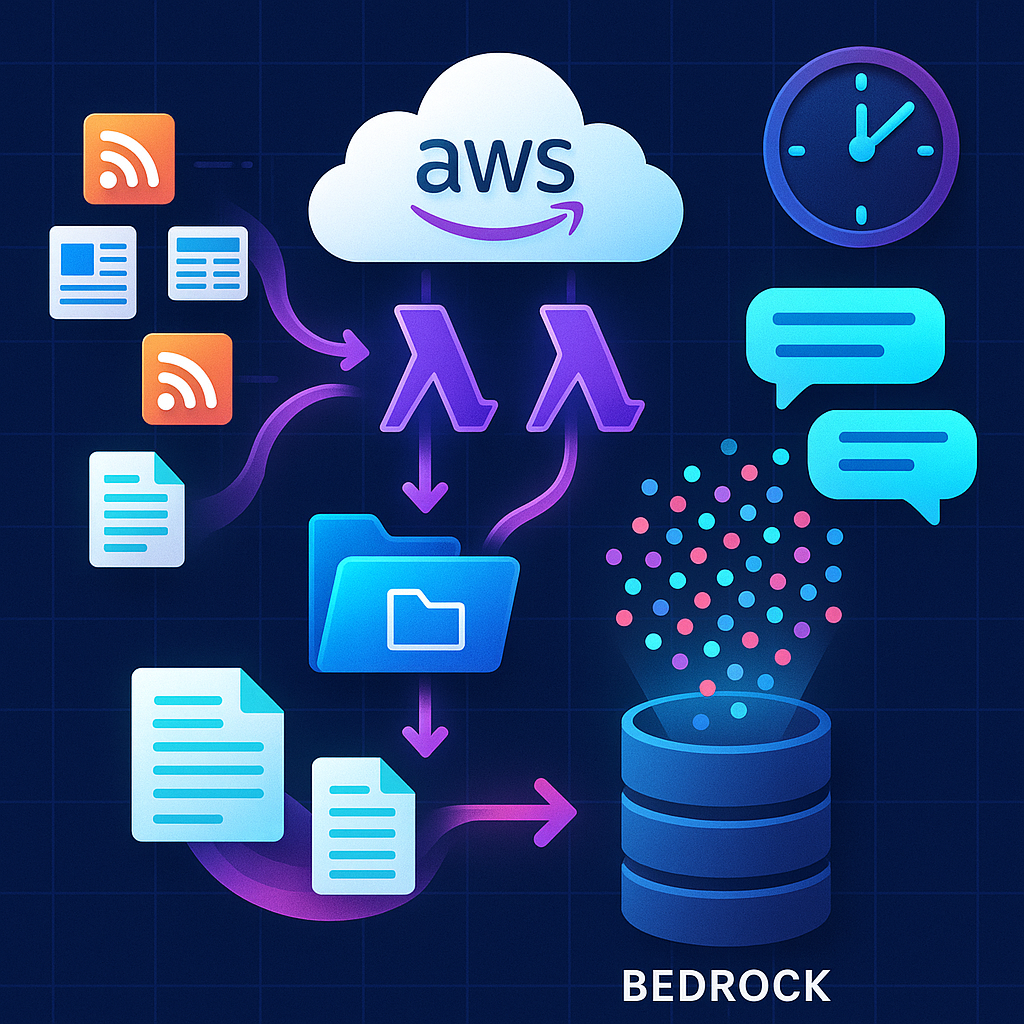
- Fetcher Lambda: Triggered on a schedule, retrieves articles from Yahoo News RSS feeds, processes them, and uploads to S3
- Syncer Lambda: Triggered by the Fetcher Lambda, starts an ingestion job in AWS Bedrock Knowledge Base
This design follows the single-responsibility principle, making each component focused and maintainable.
Infrastructure as Code with Terraform#
The entire infrastructure is defined using Terraform, enabling consistent deployments and making the solution reproducible. Let’s break down the key components:
Core Resources#
# S3 Bucket for article storage
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "demo" {
bucket = local.bucket_name
tags = local.common_tags
}
# Enable versioning and encryption
resource "aws_s3_bucket_versioning" "demo" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.demo.id
versioning_configuration {
status = "Enabled"
}
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_server_side_encryption_configuration" "demo" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.demo.id
rule {
apply_server_side_encryption_by_default {
sse_algorithm = "AES256"
}
}
}
The S3 bucket serves as the central storage for our news articles, with proper versioning and encryption configured to meet security best practices.
Scheduled Execution#
# Create EventBridge rule
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_rule" "schedule" {
name = var.eventbridge_rule_name
description = "Trigger fetcher Lambda at a regular schedule"
schedule_expression = var.schedule_expression
tags = local.common_tags
}
# Target the fetcher Lambda from the EventBridge rule
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_target" "fetcher_lambda" {
rule = aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.schedule.name
target_id = "TriggerFetcherLambda"
arn = aws_lambda_function.fetcher.arn
}
The system uses EventBridge (formerly CloudWatch Events) to trigger the fetcher Lambda on a configurable schedule, defaulting to every 10 minutes. This regular execution ensures your knowledge base stays up-to-date with the latest news.
The Fetcher Lambda: Content Acquisition#
The fetcher Lambda is responsible for retrieving articles from configurable news sources. Here’s the core functionality:
- Reads the last run timestamp to implement incremental processing
- Fetches and parses RSS feeds from Yahoo News
- Structures articles with metadata and content
- Uploads the processed articles to S3
- Invokes the syncer Lambda to trigger ingestion
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Step 1: Get the timestamp of the last successful run
last_run = get_last_run_timestamp()
# Step 2: Fetch and parse news feed data
raw_articles = fetch_news_feeds(YAHOO_NEWS_FEEDS.split(","))
# Step 3: Process and upload articles to S3
structured_articles = process_articles(raw_articles, last_run)
uploaded_keys = upload_articles_to_s3(structured_articles)
# Step 4: Update the last run timestamp
current_run = update_last_run_timestamp()
# Step 5: Invoke the syncer Lambda
if uploaded_keys:
invoke_syncer(uploaded_keys)
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": json.dumps(
{
"message": f"Successfully processed {len(structured_articles)} news articles",
"article_count": len(structured_articles),
"uploaded_keys": uploaded_keys,
"time_range": {"from": last_run, "to": current_run},
}
),
}
The code implements an important optimization: incremental processing. By storing the last run timestamp, it only processes new articles since the previous execution, minimizing unnecessary processing and reducing costs.
The Syncer Lambda: Knowledge Base Integration#
Once new articles are stored in S3, the syncer Lambda triggers an ingestion job in AWS Bedrock Knowledge Base:
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Extract information from the event
uploaded_keys = event.get("uploaded_keys", [])
# Verify uploaded files exist in S3
valid_files = check_uploaded_files(uploaded_keys)
# Start the ingestion job
response = start_ingestion_job()
if response and "ingestionJob" in response:
job = response["ingestionJob"]
# Create a detailed response
return {
"statusCode": 202, # Accepted
"body": json.dumps({
"message": "Ingestion job started successfully",
"job_id": job["ingestionJobId"],
"status": job["status"],
# Additional details...
}),
}
The syncer includes robust error handling and verification steps:
- It confirms that uploaded files actually exist in S3
- It handles various error conditions that might occur when starting an ingestion job
- It logs detailed information about the job for monitoring and debugging
Configuration Management and Flexibility#
The solution uses a hierarchical configuration approach:
- Default values defined in Terraform variables
- Environment-specific overrides through variable files
- Runtime configuration passed as environment variables to Lambda functions
This approach makes the solution adaptable to different environments and use cases without code changes.
# Lambda environment variables
environment {
variables = {
BUCKET_NAME = aws_s3_bucket.demo.id
S3_PREFIX_INCOMING = local.s3_prefix_incoming
YAHOO_NEWS_FEEDS = var.yahoo_news_feeds
LAMBDA_AWS_REGION = var.aws_region
CURSOR_KEY = local.cursor_key
BATCH_SIZE = var.demo_batch_size
SYNCER_FUNCTION_NAME = aws_lambda_function.syncer.function_name
BEDROCK_KB_NAME = var.bedrock_kb_name
BEDROCK_KB_ID = var.bedrock_kb_id
BEDROCK_DATA_SOURCE_ID = var.bedrock_data_source_id
}
}
Operational Considerations#
When deploying a system like this to production, there are several important considerations:
1. Content Source Limitations#
RSS feeds typically provide summaries rather than full articles. For a more comprehensive knowledge base, you might need to:
- Use web scraping (with proper permissions)
- Consider paid news API services
- Supplement with manual content curation
2. Rate Limiting and Quotas#
The system implements basic rate limiting between feed fetches, but you should be aware of:
- AWS Bedrock Knowledge Base ingestion quotas
- RSS feed provider rate limits
- AWS Lambda concurrency limits
3. Error Handling and Monitoring#
The implementation includes:
- Robust error handling with detailed logging
- Job tracking for Bedrock ingestion jobs
- Structured Lambda responses for easier troubleshooting
For production use, adding CloudWatch alarms and dashboards would provide better operational visibility.
Here are the proofread and restructured paragraphs for your closing sections:
Real-World Applications#
This pipeline adapts to numerous business scenarios:
- News Services: Keep your AI updated with the latest articles
- Internal Knowledge Bases: Automatically ingest company documentation
- Product Catalogs: Ensure your AI knows about new offerings
- Customer Support: Feed in new troubleshooting procedures or FAQs
Extending the Solution#
This implementation can be extended in several ways:
- Multiple Data Sources: Add support for different content sources beyond RSS feeds
- Content Preprocessing: Implement text summarization or entity extraction before ingestion
- Multi-Environment Support: Add deployment pipelines for dev/staging/prod environments
- Content Filtering: Add filtering logic to focus on specific topics or categories
Taking It Further#
While our demo uses Yahoo News feeds, you could extend this system to:
- Connect to your actual data sources
- Add preprocessing steps for document chunking and cleaning
- Implement validation before ingestion
- Add monitoring and alerting for failed ingestion jobs
Conclusion#
Building a reliable, automated RAG ingestion pipeline is essential for maintaining up-to-date AI applications. The solution presented here provides a solid foundation that you can adapt to your specific needs.
The architecture balances simplicity with robustness, using AWS managed services to minimize operational overhead while providing the flexibility needed for various use cases.
This automated RAG ingestion system demonstrates the power of connecting AWS services to keep AI systems current with minimal overhead. The serverless architecture ensures cost-effectiveness, while the scheduled nature guarantees freshness without manual intervention.
By implementing this pipeline, you’ll ensure your RAG system always has access to fresh, relevant data, significantly improving the quality of AI-generated responses as your data grows and evolves.
# (terraform/locals.tf)
locals {
# Generate a random suffix if bucket_name is not provided
bucket_suffix = var.bucket_name == "" ? random_id.bucket_suffix[0].hex : ""
bucket_name = var.bucket_name == "" ? "${var.project}-rag-demo-${local.bucket_suffix}" : var.bucket_name
# Common tags to apply to all resources
common_tags = merge({
Project = var.project
Environment = "demo"
ManagedBy = "Terraform"
}, var.tags)
# Lambda common settings
lambda_runtime = "python3.11"
lambda_handler = "main.lambda_handler"
lambda_timeout = 300
lambda_memory_size = 128
# S3 settings
s3_prefix_incoming = var.s3_prefix_incoming
cursor_key = "state/cursor.json"
# Lambda path - adjust based on your directory structure
lambda_src_path = "${path.module}/../codebase/lambda"
}
# terraform/outputs.tf
output "bucket_name" {
description = "Name of the S3 bucket created"
value = aws_s3_bucket.demo.id
}
output "fetcher_name" {
description = "Name of the fetcher Lambda function"
value = aws_lambda_function.fetcher.function_name
}
output "syncer_name" {
description = "Name of the syncer Lambda function"
value = aws_lambda_function.syncer.function_name
}
output "region" {
description = "AWS region used for deployment"
value = var.aws_region
}
output "schedule_rule" {
description = "Name of the EventBridge rule"
value = aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.schedule.name
}
# terraform/variables.tf
variable "project" {
description = "Project name"
type = string
default = "kb-demo"
}
variable "aws_region" {
description = "AWS region for deployment"
type = string
default = "us-east-1"
}
variable "aws_profile" {
description = "AWS CLI profile to use"
type = string
default = "default"
}
variable "eventbridge_rule_name" {
description = "Name for the EventBridge rule"
type = string
default = "rag_hourly_ingest_eb"
}
variable "fetcher_lambda_name" {
description = "Name for the fetcher Lambda function"
type = string
default = "fetcher_lambda"
}
variable "yahoo_news_feeds" {
description = "Comma-separated list of Yahoo News RSS feed URLs"
type = string
default = "https://www.yahoo.com/news/rss,https://www.yahoo.com/news/world/rss"
}
variable "syncer_lambda_name" {
description = "Name for the syncer Lambda function"
type = string
default = "syncer_lambda"
}
variable "bedrock_kb_name" {
description = "Name of the Bedrock Knowledge Base (informational only)"
type = string
default = "knowledge-base-quick-start-5d3h3"
}
variable "bedrock_kb_id" {
description = "ID of the Bedrock Knowledge Base"
type = string
sensitive = true
}
variable "bedrock_data_source_id" {
description = "ID of the Bedrock Knowledge Base Data Source (optional)"
type = string
sensitive = true
default = ""
}
variable "bucket_name" {
description = "S3 bucket name (optional, will be auto-generated if not provided)"
type = string
sensitive = true
default = ""
}
variable "s3_prefix_incoming" {
description = "S3 prefix for incoming documents"
type = string
default = "incoming/"
}
variable "schedule_expression" {
description = "EventBridge schedule expression"
type = string
default = "rate(10 minutes)"
}
variable "demo_batch_size" {
description = "Number of chunks to upload per fetcher invocation"
type = number
default = 1
}
variable "tags" {
description = "Tags to apply to all resources"
type = map(string)
default = {}
}
# terraform/versions.tf
terraform {
required_version = ">= 1.6"
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = ">= 5.50.0"
}
archive = {
source = "hashicorp/archive"
version = ">= 2.3.0"
}
random = {
source = "hashicorp/random"
version = ">= 3.5.0"
}
}
}
provider "aws" {
region = var.aws_region
profile = var.aws_profile
}
# Random suffix for the S3 bucket name
resource "random_id" "bucket_suffix" {
count = var.bucket_name == "" ? 1 : 0
byte_length = 4
}
# S3 Bucket
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "demo" {
bucket = local.bucket_name
tags = local.common_tags
}
# Enable versioning for the S3 bucket
resource "aws_s3_bucket_versioning" "demo" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.demo.id
versioning_configuration {
status = "Enabled"
}
}
# Server-side encryption for the S3 bucket
resource "aws_s3_bucket_server_side_encryption_configuration" "demo" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.demo.id
rule {
apply_server_side_encryption_by_default {
sse_algorithm = "AES256"
}
}
}
# Create EventBridge rule
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_rule" "schedule" {
name = var.eventbridge_rule_name
description = "Trigger fetcher Lambda at a regular schedule"
schedule_expression = var.schedule_expression
tags = local.common_tags
}
# Target the fetcher Lambda from the EventBridge rule
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_target" "fetcher_lambda" {
rule = aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.schedule.name
target_id = "TriggerFetcherLambda"
arn = aws_lambda_function.fetcher.arn
}
# Permission for EventBridge to invoke the fetcher Lambda
resource "aws_lambda_permission" "allow_eventbridge" {
statement_id = "AllowExecutionFromEventBridge"
action = "lambda:InvokeFunction"
function_name = aws_lambda_function.fetcher.function_name
principal = "events.amazonaws.com"
source_arn = aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.schedule.arn
}
# Create fetcher Lambda function
data "archive_file" "fetcher_zip" {
type = "zip"
source_dir = "${local.lambda_src_path}/fetcher"
output_path = "${path.module}/fetcher.zip"
}
resource "aws_lambda_function" "fetcher" {
function_name = var.fetcher_lambda_name
role = aws_iam_role.fetcher_lambda.arn
handler = local.lambda_handler
runtime = local.lambda_runtime
timeout = local.lambda_timeout
memory_size = local.lambda_memory_size
filename = data.archive_file.fetcher_zip.output_path
source_code_hash = data.archive_file.fetcher_zip.output_base64sha256
environment {
variables = {
BUCKET_NAME = aws_s3_bucket.demo.id
S3_PREFIX_INCOMING = local.s3_prefix_incoming
CURSOR_KEY = local.cursor_key
BATCH_SIZE = var.demo_batch_size
SYNCER_FUNCTION = var.syncer_lambda_name
LAMBDA_AWS_REGION = var.aws_region
YAHOO_NEWS_FEEDS = var.yahoo_news_feeds
BEDROCK_KB_ID = var.bedrock_kb_id
BEDROCK_DATA_SOURCE_ID = var.bedrock_data_source_id
}
}
tags = local.common_tags
}
# Create syncer Lambda function
data "archive_file" "syncer_zip" {
type = "zip"
source_dir = "${local.lambda_src_path}/syncer"
output_path = "${path.module}/syncer.zip"
}
resource "aws_lambda_function" "syncer" {
function_name = var.syncer_lambda_name
role = aws_iam_role.syncer_lambda.arn
handler = local.lambda_handler
runtime = local.lambda_runtime
timeout = local.lambda_timeout
memory_size = local.lambda_memory_size
filename = data.archive_file.syncer_zip.output_path
source_code_hash = data.archive_file.syncer_zip.output_base64sha256
environment {
variables = {
BUCKET_NAME = aws_s3_bucket.demo.id
S3_PREFIX_INCOMING = local.s3_prefix_incoming
LAMBDA_AWS_REGION = var.aws_region
BEDROCK_KB_NAME = var.bedrock_kb_name
BEDROCK_KB_ID = var.bedrock_kb_id
BEDROCK_DATA_SOURCE_ID = var.bedrock_data_source_id
}
}
tags = local.common_tags
}
# IAM Role for fetcher Lambda
resource "aws_iam_role" "fetcher_lambda" {
name = "${var.fetcher_lambda_name}_role"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Action = "sts:AssumeRole"
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = {
Service = "lambda.amazonaws.com"
}
}
]
})
tags = local.common_tags
}
# IAM Role for syncer Lambda
resource "aws_iam_role" "syncer_lambda" {
name = "${var.syncer_lambda_name}_role"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Action = "sts:AssumeRole"
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = {
Service = "lambda.amazonaws.com"
}
}
]
})
tags = local.common_tags
}
# CloudWatch Logs policy for fetcher Lambda
resource "aws_iam_policy" "fetcher_logs" {
name = "${var.fetcher_lambda_name}_logs_policy"
description = "IAM policy for fetcher Lambda logging"
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
]
Resource = "arn:aws:logs:*:*:*"
}
]
})
}
# CloudWatch Logs policy for syncer Lambda
resource "aws_iam_policy" "syncer_logs" {
name = "${var.syncer_lambda_name}_logs_policy"
description = "IAM policy for syncer Lambda logging"
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
]
Resource = "arn:aws:logs:*:*:*"
}
]
})
}
# S3 access policy for fetcher Lambda
resource "aws_iam_policy" "fetcher_s3" {
name = "${var.fetcher_lambda_name}_s3_policy"
description = "IAM policy for fetcher Lambda S3 access"
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"s3:ListBucket"
]
Resource = aws_s3_bucket.demo.arn
},
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:PutObjectTagging"
]
Resource = "${aws_s3_bucket.demo.arn}/*"
}
]
})
}
# S3 access policy for syncer Lambda
resource "aws_iam_policy" "syncer_s3" {
name = "${var.syncer_lambda_name}_s3_policy"
description = "IAM policy for syncer Lambda S3 access"
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"s3:ListBucket"
]
Resource = aws_s3_bucket.demo.arn
},
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"s3:GetObject"
]
Resource = "${aws_s3_bucket.demo.arn}/*"
}
]
})
}
# Lambda invoke policy for fetcher Lambda
resource "aws_iam_policy" "fetcher_invoke" {
name = "${var.fetcher_lambda_name}_invoke_policy"
description = "IAM policy for fetcher Lambda to invoke syncer Lambda"
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"lambda:InvokeFunction"
]
Resource = aws_lambda_function.syncer.arn
}
]
})
}
# Bedrock KB access policy for syncer Lambda (only if KB ID is provided)
resource "aws_iam_policy" "syncer_bedrock" {
count = var.bedrock_kb_id != "" ? 1 : 0
name = "${var.syncer_lambda_name}_bedrock_policy"
description = "IAM policy for syncer Lambda Bedrock KB access"
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"bedrock:StartIngestionJob",
"bedrock:GetIngestionJob",
"bedrock:ListIngestionJobs"
]
Resource = "arn:aws:bedrock:${var.aws_region}:${data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id}:knowledge-base/${var.bedrock_kb_id}"
}
]
})
}
# Get AWS account ID
data "aws_caller_identity" "current" {}
# Attach policies to roles
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "fetcher_logs" {
role = aws_iam_role.fetcher_lambda.name
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.fetcher_logs.arn
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "fetcher_s3" {
role = aws_iam_role.fetcher_lambda.name
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.fetcher_s3.arn
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "fetcher_invoke" {
role = aws_iam_role.fetcher_lambda.name
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.fetcher_invoke.arn
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "syncer_logs" {
role = aws_iam_role.syncer_lambda.name
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.syncer_logs.arn
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "syncer_s3" {
role = aws_iam_role.syncer_lambda.name
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.syncer_s3.arn
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "syncer_bedrock" {
count = var.bedrock_kb_id != "" ? 1 : 0
role = aws_iam_role.syncer_lambda.name
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.syncer_bedrock[0].arn
}
#!/bin/bash
# cleanup.sh
#!/bin/bash
# Cleanup script for Terraform resources
# Set the AWS profile
export AWS_PROFILE=munnoo
export AWS_REGION=us-east-1
export TF_VAR_project="rag_hourly_ingest_claude"
export TF_VAR_aws_region="$AWS_REGION"
export TF_VAR_aws_profile="$AWS_PROFILE"
export TF_VAR_eventbridge_rule_name="rag_hourly_ingest_eb"
export TF_VAR_fetcher_lambda_name="fetcher_lambda"
export TF_VAR_syncer_lambda_name="syncer_lambda"
export TF_VAR_bedrock_kb_name="knowledge-base-quick-start-5d3h3"
export TF_VAR_bedrock_kb_id="8FYOHD0OOA" # sensitive
export TF_VAR_bedrock_data_source_id="JHA7ZKEA48" # optional, sensitive
export TF_VAR_bucket_name="khalidrizvi-rag-houry-ingest-claude" # optional fixed name (sensitive), else empty for auto-generate
export TF_VAR_s3_prefix_incoming="incoming/"
export TF_VAR_schedule_expression="rate(10 minutes)"
export TF_VAR_demo_batch_size=1
cd terraform
# Get outputs
REGION=$(terraform output -raw region)
BUCKET=$(terraform output -raw bucket_name)
echo "Emptying S3 bucket s3://${BUCKET} ..."
aws s3 rm "s3://${BUCKET}" --recursive --region "$REGION" --profile munnoo
echo "Destroying Terraform resources..."
terraform destroy -auto-approve
echo "Cleanup complete!"
#!/bin/bash
#deploy.sh
#!/bin/bash
# Environment setup for Terraform deployment
export AWS_PROFILE=profile
export AWS_REGION=region
export TF_VAR_project="rag_hourly_ingest_claude"
export TF_VAR_aws_region="$AWS_REGION"
export TF_VAR_aws_profile="$AWS_PROFILE"
export TF_VAR_eventbridge_rule_name="rag_hourly_ingest_eb"
export TF_VAR_fetcher_lambda_name="fetcher_lambda"
export TF_VAR_syncer_lambda_name="syncer_lambda"
export TF_VAR_bedrock_kb_name="dummy_kb"
export TF_VAR_bedrock_kb_id="kb_id" # sensitive
export TF_VAR_bedrock_data_source_id="ds_id" # optional, sensitive
export TF_VAR_bucket_name="s3_bucket_name" # optional fixed name (sensitive), else empty for auto-generate
export TF_VAR_s3_prefix_incoming="incoming/"
export TF_VAR_schedule_expression="rate(10 minutes)"
export TF_VAR_demo_batch_size=1
# Install dependencies for Lambda functions
echo "Installing Lambda dependencies..."
pip install -r requirements.txt --target ./codebase/lambda/fetcher/ --ignore-installed
# If syncer also needs dependencies, install them too
pip install -r requirements.txt --target ./codebase/lambda/fetcher/ --ignore-installed
# Deploy instructions
cd terraform
terraform init
terraform plan -out plan.tfplan
terraform apply plan.tfplan
# Smoke test without waiting 10 minutes:
REGION=$(terraform output -raw region)
FETCHER=$(terraform output -raw fetcher_name)
aws lambda invoke --function-name "$FETCHER" --payload '{}' out.json --region "$REGION" >/dev/null
cat out.json
BUCKET=$(terraform output -raw bucket_name)
aws s3 ls "s3://${BUCKET}/incoming/" --recursive --region "$REGION"
# View CloudWatch logs for the Lambda functions
echo "View fetcher Lambda logs:"
echo "aws logs filter-log-events --log-group-name /aws/lambda/$FETCHER --region $REGION"
echo "View syncer Lambda logs:"
echo "aws logs filter-log-events --log-group-name /aws/lambda/$(terraform output -raw syncer_name) --region $REGION"
# codebase/fetcher.py
import os
import boto3
import json
import logging
import requests
import feedparser
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from email.utils import parsedate_to_datetime
from hashlib import md5
import time
# Configure logging
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# Environment variables
BUCKET_NAME = os.environ["BUCKET_NAME"]
S3_PREFIX_INCOMING = os.environ["S3_PREFIX_INCOMING"]
LAST_RUN_KEY = os.environ["CURSOR_KEY"] # Repurposing cursor for timestamp
SYNCER_FUNCTION = os.environ["SYNCER_FUNCTION"]
YAHOO_NEWS_FEEDS = os.environ.get(
"YAHOO_NEWS_FEEDS",
"https://www.yahoo.com/news/rss,https://www.yahoo.com/news/world/rss",
)
# Initialize AWS clients
s3_client = boto3.client("s3")
lambda_client = boto3.client("lambda")
def get_last_run_timestamp():
"""Read the last run timestamp from S3."""
try:
response = s3_client.get_object(Bucket=BUCKET_NAME, Key=LAST_RUN_KEY)
content = json.loads(response["Body"].read())
return content.get("last_run", None)
except s3_client.exceptions.NoSuchKey:
# If this is our first run, use a timestamp from 1 hour ago
default_time = (datetime.utcnow() - timedelta(hours=1)).isoformat()
logger.info(f"No previous run record found, defaulting to {default_time}")
return default_time
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error reading last run timestamp: {str(e)}")
# Fallback to 1 hour ago if there's any error
return (datetime.utcnow() - timedelta(hours=1)).isoformat()
def update_last_run_timestamp():
"""Write the current timestamp to S3 as our new 'last run' marker."""
current_time = datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
content = {"last_run": current_time, "updated_at": current_time}
s3_client.put_object(
Bucket=BUCKET_NAME,
Key=LAST_RUN_KEY,
Body=json.dumps(content),
ContentType="application/json",
)
logger.info(f"Updated last run timestamp to {current_time}")
return current_time
def fetch_yahoo_news(last_run_timestamp):
"""Fetch news from Yahoo RSS feeds published since the last run."""
feeds = YAHOO_NEWS_FEEDS.split(",")
last_run = datetime.fromisoformat(last_run_timestamp)
all_articles = []
logger.info(f"Fetching news published after {last_run_timestamp}")
for feed_url in feeds:
try:
logger.info(f"Processing feed: {feed_url}")
# Add a small delay to avoid rate limiting
time.sleep(1)
# Parse the RSS feed
feed = feedparser.parse(feed_url)
if hasattr(feed, "status") and feed.status != 200:
logger.warning(
f"Feed returned non-200 status: {feed.status}, URL: {feed_url}"
)
continue
# Filter for entries newer than our last run
new_entries = []
for entry in feed.entries:
# Yahoo RSS uses 'published' for the publication date
if "published" in entry:
try:
# Parse RFC822 date format used in RSS
pub_date = parsedate_to_datetime(entry.published)
# Only keep entries newer than our last run
if pub_date > last_run:
new_entries.append(entry)
except Exception as e:
logger.warning(
f"Could not parse publication date: {entry.published}, error: {str(e)}"
)
# If we can't parse the date, include it to be safe
new_entries.append(entry)
else:
# If there's no publication date, include it to be safe
new_entries.append(entry)
logger.info(f"Found {len(new_entries)} new articles in {feed_url}")
all_articles.extend(new_entries)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error processing feed {feed_url}: {str(e)}")
return all_articles
def structure_article(entry, source_url):
"""Convert a feedparser entry into a structured article for our knowledge base."""
# Create a unique ID for the article
if hasattr(entry, "id"):
article_id = entry.id
else:
# If no ID exists, create one from the title and link
article_id = md5((entry.title + entry.link).encode()).hexdigest()
# Extract the publication date
if hasattr(entry, "published"):
try:
pub_date = parsedate_to_datetime(entry.published).isoformat()
except:
pub_date = datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
else:
pub_date = datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
# Extract the content
content = ""
if hasattr(entry, "content"):
content = entry.content[0].value
elif hasattr(entry, "summary"):
content = entry.summary
elif hasattr(entry, "description"):
content = entry.description
# Create a structured article document
article = {
"id": article_id,
"title": entry.title,
"link": entry.link,
"published_date": pub_date,
"content": content,
"source": {"name": "Yahoo News", "url": source_url},
"fetched_at": datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
}
# Add categories if available
if hasattr(entry, "tags"):
article["categories"] = [tag.term for tag in entry.tags]
# Add author if available
if hasattr(entry, "author"):
article["author"] = entry.author
return article
def upload_articles_to_s3(articles):
"""Upload structured news articles to S3."""
uploaded_keys = []
for article in articles:
# Create a filename based on publication date and ID for easy sorting
pub_date = datetime.fromisoformat(
article["published_date"].replace("Z", "+00:00")
if article["published_date"].endswith("Z")
else article["published_date"]
)
filename = f"{pub_date.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')}/{article['id']}.json"
s3_key = f"{S3_PREFIX_INCOMING}{filename}"
# Upload to S3
s3_client.put_object(
Bucket=BUCKET_NAME,
Key=s3_key,
Body=json.dumps(article),
ContentType="application/json",
)
uploaded_keys.append(s3_key)
logger.info(
f"Uploaded article: {article['title']} to s3://{BUCKET_NAME}/{s3_key}"
)
return uploaded_keys
def invoke_syncer(uploaded_keys):
"""Invoke the syncer Lambda with the list of uploaded keys."""
if not uploaded_keys:
logger.info("No articles uploaded, skipping syncer invocation")
return
payload = {
"uploaded_keys": uploaded_keys,
"source": "yahoo_news",
"timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
}
try:
response = lambda_client.invoke(
FunctionName=SYNCER_FUNCTION,
InvocationType="Event", # Asynchronous invocation
Payload=json.dumps(payload),
)
logger.info(f"Invoked syncer Lambda {SYNCER_FUNCTION} asynchronously")
return response
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error invoking syncer: {str(e)}")
return None
def lambda_handler(event, context):
"""
Main Lambda handler function:
1. Get the timestamp of the last run
2. Fetch Yahoo News articles published since then
3. Structure and upload articles to S3
4. Update the last run timestamp
5. Trigger the syncer to update our knowledge base
"""
logger.info(f"Yahoo News Fetcher Lambda triggered with event: {json.dumps(event)}")
# Step 1: Get the last run timestamp
last_run = get_last_run_timestamp()
# Step 2: Fetch news from Yahoo
articles_raw = fetch_yahoo_news(last_run)
if not articles_raw:
logger.info("No new articles found since the last run")
# Still update the timestamp even if no new articles
current_run = update_last_run_timestamp()
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": json.dumps(
{
"message": "No new articles found",
"time_range": {"from": last_run, "to": current_run},
}
),
}
# Step 3: Structure articles and upload to S3
structured_articles = [
structure_article(entry, source_url)
for entry in articles_raw
for source_url in YAHOO_NEWS_FEEDS.split(",")
]
uploaded_keys = upload_articles_to_s3(structured_articles)
# Step 4: Update the last run timestamp
current_run = update_last_run_timestamp()
# Step 5: Invoke the syncer Lambda
if uploaded_keys:
invoke_syncer(uploaded_keys)
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": json.dumps(
{
"message": f"Successfully processed {len(structured_articles)} news articles",
"article_count": len(structured_articles),
"uploaded_keys": uploaded_keys,
"time_range": {"from": last_run, "to": current_run},
}
),
}
# codebase/syncer.py
import os
import boto3
import json
import logging
from botocore.exceptions import ClientError
from datetime import datetime
# Configure logging
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# Environment variables
BUCKET_NAME = os.environ["BUCKET_NAME"]
S3_PREFIX_INCOMING = os.environ["S3_PREFIX_INCOMING"]
AWS_REGION = os.environ.get("LAMBDA_AWS_REGION", "us-east-1") # Changed from AWS_REGION
BEDROCK_KB_NAME = os.environ["BEDROCK_KB_NAME"]
BEDROCK_KB_ID = os.environ["BEDROCK_KB_ID"]
BEDROCK_DATA_SOURCE_ID = os.environ.get("BEDROCK_DATA_SOURCE_ID", "")
# Initialize AWS clients
s3_client = boto3.client("s3", region_name=AWS_REGION)
bedrock_agent = boto3.client("bedrock-agent", region_name=AWS_REGION)
def start_ingestion_job():
"""Start a Bedrock Knowledge Base ingestion job."""
if not BEDROCK_KB_ID:
logger.warning("BEDROCK_KB_ID is not set, skipping ingestion")
return None
try:
# Prepare params for the API call
params = {
"knowledgeBaseId": BEDROCK_KB_ID,
}
# Only add dataSourceId if it's provided
if BEDROCK_DATA_SOURCE_ID:
params["dataSourceId"] = BEDROCK_DATA_SOURCE_ID
logger.info(
f"Starting ingestion job for KB ID: {BEDROCK_KB_ID}, Data Source ID: {BEDROCK_DATA_SOURCE_ID}"
)
else:
logger.info(
f"Starting ingestion job for KB ID: {BEDROCK_KB_ID} (no Data Source ID provided)"
)
# Log attempt to start ingestion
logger.info(
f"Attempting to start ingestion job with params: {json.dumps(params)}"
)
# Call the Bedrock API
response = bedrock_agent.start_ingestion_job(params)
# Log success
job_id = response["ingestionJob"]["ingestionJobId"]
status = response["ingestionJob"]["status"]
logger.info(
f"Ingestion job started successfully: {job_id}, initial status: {status}"
)
# Record additional details about the job
try:
job_details = {
"job_id": job_id,
"status": status,
"started_at": datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
"kb_id": BEDROCK_KB_ID,
"kb_name": BEDROCK_KB_NAME,
}
# Store job details in S3 for tracking purposes
s3_client.put_object(
Bucket=BUCKET_NAME,
Key=f"jobs/{job_id}.json",
Body=json.dumps(job_details),
ContentType="application/json",
)
except Exception as e:
# Non-critical error - job is still running even if we can't save details
logger.warning(f"Could not save job details to S3: {str(e)}")
return response
except ClientError as e:
error_code = e.response["Error"]["Code"]
error_message = e.response["Error"]["Message"]
logger.error(f"Error starting ingestion job: {error_code} - {error_message}")
logger.error(f"Full error response: {json.dumps(e.response)}")
return {"error": error_code, "message": error_message}
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Unexpected error: {str(e)}")
return {"error": "UnexpectedException", "message": str(e)}
def check_uploaded_files(uploaded_keys):
"""Verify that the uploaded files exist in S3 and log information about them."""
if not uploaded_keys:
logger.info("No uploaded files to check")
return 0
valid_files = 0
for s3_key in uploaded_keys:
try:
# Check if the file exists
response = s3_client.head_object(Bucket=BUCKET_NAME, Key=s3_key)
size = response.get("ContentLength", 0)
last_modified = (
response.get("LastModified", "").isoformat()
if hasattr(response.get("LastModified", ""), "isoformat")
else "unknown"
)
logger.info(
f"Verified file exists: s3://{BUCKET_NAME}/{s3_key}, Size: {size} bytes, Last Modified: {last_modified}"
)
valid_files += 1
except Exception as e:
logger.warning(
f"File not found or cannot be accessed: s3://{BUCKET_NAME}/{s3_key}, Error: {str(e)}"
)
logger.info(f"Verified {valid_files} out of {len(uploaded_keys)} files")
return valid_files
def lambda_handler(event, context):
"""
Main Lambda handler function.
1. Processes the event from the fetcher Lambda
2. Validates uploaded files exist in S3
3. Starts a Bedrock KB ingestion job
"""
logger.info(f"Syncer Lambda triggered with event: {json.dumps(event)}")
# Extract information from the event
uploaded_keys = event.get("uploaded_keys", [])
source = event.get("source", "unknown")
timestamp = event.get("timestamp", datetime.utcnow().isoformat())
# Log information about the files being ingested
logger.info(
f"Preparing to process {len(uploaded_keys)} files from source: {source}"
)
# Verify uploaded files exist in S3
valid_files = check_uploaded_files(uploaded_keys)
if valid_files == 0 and len(uploaded_keys) > 0:
logger.warning("None of the specified files could be found in S3")
return {
"statusCode": 404,
"body": json.dumps(
{
"message": "No valid files found to ingest",
"uploaded_keys": uploaded_keys,
}
),
}
# Start the ingestion job
response = start_ingestion_job()
if response and "ingestionJob" in response:
job = response["ingestionJob"]
# Create a detailed response with information about what's being ingested
return {
"statusCode": 202, # Accepted
"body": json.dumps(
{
"message": "Ingestion job started successfully",
"job_id": job["ingestionJobId"],
"status": job["status"],
"kb_name": BEDROCK_KB_NAME,
"kb_id": BEDROCK_KB_ID,
"data_source_id": BEDROCK_DATA_SOURCE_ID or "Not specified",
"files_processed": valid_files,
"source": source,
"timestamp": timestamp,
}
),
}
elif response and "error" in response:
return {
"statusCode": 500,
"body": json.dumps(
{
"message": "Failed to start ingestion job",
"error": response["error"],
"details": response["message"],
"files_processed": valid_files,
"source": source,
}
),
}
else:
return {
"statusCode": 204, # No Content
"body": json.dumps(
{
"message": "No ingestion job was started (BEDROCK_KB_ID not configured)",
"files_processed": valid_files,
"source": source,
}
),
}
Important Considerations#
No API Key Required: Unlike many news services, Yahoo News RSS feeds don’t require authentication, making this solution simple to deploy.
Rate Limiting: I’ve added a small delay between feed fetches to avoid potential rate limiting, but Yahoo doesn’t publish specific limits for their RSS feeds.
Content Limitations: RSS feeds typically provide summaries rather than full articles. If you need complete article content, you might need to:
- Use a web scraping approach (with proper permissions)
- Consider a paid news API service
Historical Data: RSS feeds only contain recent articles. For historical data going back to 1999, you would need:
- A one-time data import from an archive service
- A commercial news database subscription
Error Handling: The code includes robust error handling to ensure the function continues running even if individual feeds fail.
Time Zones: RSS dates are standardized in RFC822 format, which the function correctly parses to maintain accurate timestamps.
This implementation gives you a solid foundation for keeping your knowledge base updated with the latest news from Yahoo, without requiring any API keys or paid services. The fetcher is designed to be reliable, efficient, and to work seamlessly with your existing syncer function to maintain an up-to-date knowledge base for your RAG system.
